
What is On-page SEO?
On-page SEO (sometimes known as “On-site SEO”) is the technique of optimizing individual web pages in search engines in order to rank better and generate more relevant traffic. In contrast to off-page SEO, which refers to links and other external signals, on-page SEO refers to both the content and HTML source code of a website that may be improved. On-page SEO strategies often used include improving title tags, content, internal links, and URLs.
Important On page SEO factors:

Importance of On-page SEO:
SEO assists search engines in analyzing your website and the information associated with it in order to determine if a searcher’s query is relevant to your site. Google’s algorithm is continually being updated in order to better comprehend a searcher’s intent and produce search results that fit that user’s demands. Your website should evolve in tandem with Google’s algorithm. It is critical that your website and its content are optimized to the newest methods employed by firms such as Google and Bing, including what is visible to users (i.e. media, content, photos) and what is visible to search engines (i.e. metadata, HTML). This allows search engines to comprehend your site and determine how to rank it.
Now that you understand why on-page SEO is still important, it’s time to begin optimizing your content. Also, understand what is the importance of SEO?
How to optimize your content?
In the first 100 words, use your target keyword:
This is an old-school on-page SEO strategy that still works. Simply utilize your core keyword once in the first 100-150 words of your post. For example, in my essay optimized for the phrase “email marketing,” I started it straight away. Google gives greater weight to phrases that are towards the top of your page. That makes sense. Assume you recently published an article about The Keto Diet. Would it make sense to include the word “keto diet” halfway down the page if your article was truly about The Keto Diet? Obviously not. This is why you should include your keyword inside the first 100 words or so. This is one of those minor details that aid Google in understanding what your page is about.
Wrap the title of your blog post with an H1 tag:
The H1 tag functions are similar to a small title tag. Indeed, Google has indicated that utilizing an H1 tag “assists Google in understanding the structure of the page.” The H1 tag is automatically added to your blog post title by most systems (including WordPress). If that’s the case, you’re good to go. However, this is not always the case. Check the code of your website to ensure that your title is enclosed in an H1 and that your keyword is included within the H1 tag.
Wrap Subheadings in H2 Tags:
Include at least one subheading with your goal keyword. And then put an H2 tag around that subheading. Is an H2 tag going to make or destroy your on-page SEO? No. However, it can’t harm. My personal SEO studies have found that enclosing your target term in an H2 element can help. Here’s an example of how to use this strategy: target keyword= “content marketing tools.”
Keyword Frequency:
This is exactly what it sounds like: it is the number of times your keyword occurs in your text. Google may deny that repeating the same keyword helps. However, experienced SEO professionals will tell you that it does work. Consider the following: Assume you have a page that Google believes is about a certain term. However, that keyword occurs just once on the website. How certain are they that the page is about that keyword? Not at all. On the other hand, if the website uses the term ten times, Google may feel more confident in the topic of that page. To be clear, this isn’t about keyword stuffing, but stating your goal keyword a couple of times to show Google that your content is indeed about that subject.
Use External (Outbound) Links:
External links to relevant pages assist Google in determining the topic of your page. It also shows Google that your page is a good source of information. And this isn’t simply a hypothesis. Reboot Online conducted an experiment to evaluate if external links aided in ranking improvement. They built ten new websites. Half of the websites had links to authority sites (like Oxford University). The remaining half was devoid of external linkages. And websites with external links outperform those without.
Optimize Your URL Structure for SEO:
URL structure is an underappreciated aspect of on-page SEO. Yes, Google started using strange URL variations in search results a while ago. Even so, the terms you put in your URL appear here. In addition, URLs in mobile and desktop SERPs are now shown above the title tag. As a result, I’d argue that your URL is now more crucial than ever.
With that, here’s how to create SEO-friendly URLs:
- Make your URLs short
- Include a keyword in every URL
That’s it.
Title Tags
The title tag is an HTML tag that appears in the head section of every webpage. It gives an initial hint or context as to what the thematic subject matter of the page it is on is.
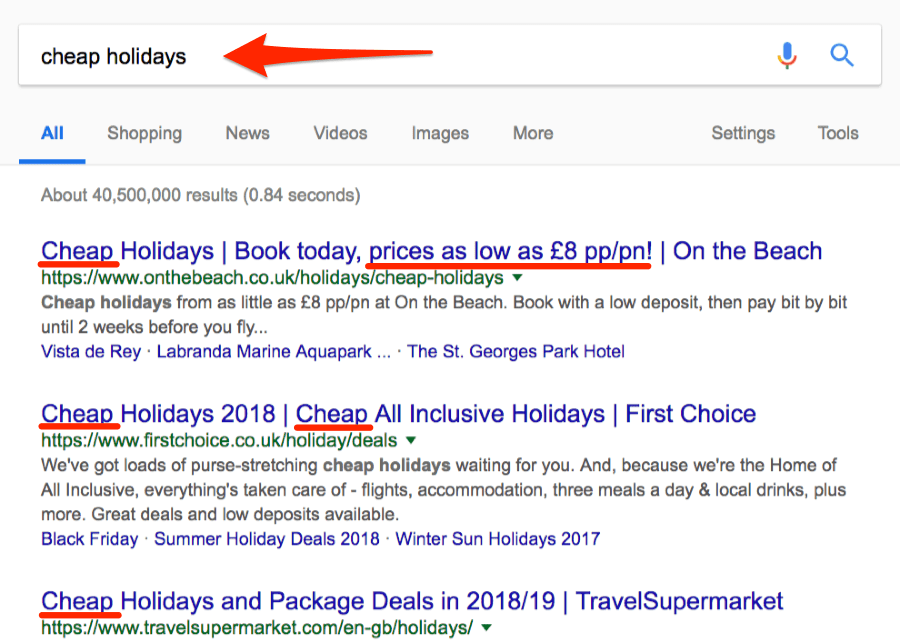
Tips for optimising title tags:
Use no more than 66 characters and keep it precise:
Search engines only display a limited number of characters from the title tag. Google displays the first 66 characters. After that, it just inserts an ellipsis. If you want your title tags to seem professional, don’t use more than 66 characters. Short titles are simpler to read than lengthy ones. The fewer words in your title tag, the more weight Google gives to each term. As a result, a keyword scoring well in a title tag of 4 words is simpler than it is in a title tag of 8 words. This is referred to as keyword density.
Put the keyword first and use title tag modifiers:
Google reportedly attributes more value to the first word in a title tag than the last one. Jakob Nielsen’s research shows that the first 11 characters determine whether someone continues to read on or not. Using title tag modifiers like best, checklist, guide, the review can help you rank on your targeted keyword.
Create appealing title tags that are unique for each page:
You’ll probably do well on Google if you load the title tag with keywords. However, it will make your title tag unappealing, and visitors will be less likely to click on it. Because the title tag is often people’s first impression of your company, make it appealing and distinct for each page. Ensure that you make a positive first impression.
Congratulations! If you follow these guidelines and make sure to add your brand name.
You have a title tag that is completely optimized. Let’s move on to description tag optimization
Description Tags
The description tag is a long paragraph that describes what a page is about. Because the description tag is frequently displayed by Google, it’s an excellent tool for persuading visitors to visit your page.
Tips for writing a great description tag:
Use no more than 155 characters in your description tag:
Google only displays the first 160 characters of your description tag. It merely inserts an ellipsis after that. If you want to be safe, limit yourself to 155 characters. Don’t forget that spaces and punctuation marks are also considered characters.
Use the following keywords to improve your page’s ranking:
The description tag is only displayed if there is a strong content relationship between the description element, the user’s query, and the page’s content.
Make sure to include the page’s keyword(s) in your description tag if you want Google to see it.
Think, Write, and Be Accurate:
First and foremost, consider your target audience, the aim of your page, and the type of description that will entice them. After you’ve gathered your thoughts, develop a succinct and persuasive descriptive title. Use additional characters to provide your readers with more information instead of repeating the title tag. It should be unique for each page and written in an appropriate language.
I am confident that if you follow these guidelines, you will be able to create persuasive description titles for your users.
UX Signals
UX signals are behavioral patterns that Google uses to assess a user’s experience on your website. The click-through rate (CTR) and bounce rate are two of the most important behavioral measures. These two variables have a significant impact on your rankings, therefore it’s critical to grasp what UX signals are and how to leverage them to your advantage.
CTR (Click Through Rate):
CTR is a percentage that describes the number of individuals who click on a specific link to get to a specific page. A high CTR indicates that your material is valuable and related to the user’s search.
CTR = (total campaign impressions * clicks on a campaign) x 100.

What makes your website worth visiting?
- Informative (the title includes your search query)
- Promising (in terms of providing the information the searcher seeks)
- Appealing to the eye (the search result stands out from the crowd).
Bounce Rate
The bounce rate is the percentage of visitors that arrive on your page and then leave without engaging with any of the content. To put it another way, it’s the number of single-page sessions divided by the total number of sessions. For a variety of reasons, a high bounce rate might have a negative impact on your rankings. It’s possible that the user didn’t find the material compelling or didn’t locate what he was seeking.

Importance of UX Signals:
These signals are important because they may reveal a lot about the quality of content on your site. When you offer high-quality material that is related to the phrases they were searching for, visitors are more likely to stay on your site longer. You can determine which pages perform well and which pages want improvement by looking at your CTR and bounce rate. You may use your CTR to determine which sites or articles are generating the most traffic. What is the topic of your content? Is it a long-form or a bite-sized presentation? What aspects of your material are most beneficial to your visitors? Do you have any relevant and useful photographs or videos? How can you utilize these high-performing pages to inspire the rest of your site’s content?
Advanced SEO tips:
Use unique images for advanced SEO (proper icons and images)
Do you utilize stock photos in your articles? Those stock photos, on the other hand, might be damaging your SEO. Shai Aharony has conducted research into the impact of stock pictures on Google results. Here’s what happened…To begin with, Shai constructed dozens of new brand-new websites specifically for these tests. These were brand new domain names that had never previously been registered. On several of these sites, he utilized generic stock pictures. On others, there were original photographs. The results were unmistakable: websites using original photographs outperformed those that used stock photos. Consider producing bespoke pictures if you’re utilizing stock photos that a thousand other websites are using. Not only would utilizing original photos assist but having the right size icons and graphics helps as well.
Internal linking:
Internal linking is extremely beneficial to SEO. You want to link from your site’s high-authority pages to sites that need to be boosted. Make careful to utilize keyword-rich anchor text when you do so. With that out of the way, here’s the method I employ and suggest. To begin, utilize an SEO tool such as Ahrefs to find the pages on your site that have the greatest link authority. Then, from those sites, add a few internal links to a high-priority page on your site.
Create in-depth content:
Google intends to display material that provides them with everything they need in one place. To put it another way, extensive content. Your article will have a better chance of ranking if it covers the full topic. The site has a possibility to rank better if your material is easy to read and comprehend for consumers, as well as keyword-rich.
Boost the speed of your website:
On record, Google has acknowledged that website loading speed is an SEO ranking indication (and they recently made PageSpeed even MORE important). Moving to a speedier host, according to our survey of 5.2 million websites, can increase your site’s loading speed. Get rid of as many third-party scripts as possible and decrease the overall size of your page.

Image Optimization:
Every picture on your site should have a meaningful filename and alt text. This aids Google (and visually challenged users) in comprehending what each image depicts. Make one image optimized around your goal term if it makes sense. As a result, utilize a filename that contains your desired term (for example, on-site SEO-chart.png). Use the same term in your picture alt tags as well. Another reason to optimize your photos for SEO is that it provides search engines another hint as to what your website is about, perhaps helping it rank higher.
A site that is mobile-friendly:
It is true that mobile-friendliness is important for SEO. In reality, when Google and Bing identify that a person is searching on a mobile device, it uses it as a ranking indication. In general, mobile-friendly websites outrank non-mobile-friendly websites in mobile search results.
NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) should be consistent across all sites:
NAP consistency is vital for local SEO since it lends validity to your business and increases your chances of ranking highly. It also exposes the most important information about your company to search engines and possibly new consumers.

Conclusion:
To recap this article, we’ve gone over all of the fundamentals you’ll need to know in order to optimize your on-page SEO and help your website rank higher. The tips provided in each blog post will assist you in becoming a master of on-page SEO optimization. Just knowing how to rank a website using on-page SEO isn’t enough; you also need to know how to rank a website using off-page SEO. Keep an eye out for our upcoming article, which will cover off-page SEO.



